Introduction to reproduction in human beings
In Standard Six, you learnt about the parts and functions of the human reproductive system. You also learnt about the changes that occur in the males and females during growth and development. In this class, you are going to learn about the process of reproduction in human beings.
Activity 1.1
Research Activity
- Find out what we require in order to reproduce.
- Write short notes in your notebook.
- Share your findings with your friends.
Reproduction is the process of giving rise to new ones of own kind. The process is important because it ensures continuity of organisms. Reproduction in human beings involves male and female gametes.
Males, after attaining the age of puberty, become sexually mature due to hormonal changes in their bodies. These hormonal changes lead to production of male gametes called sperms or spermatozoa.
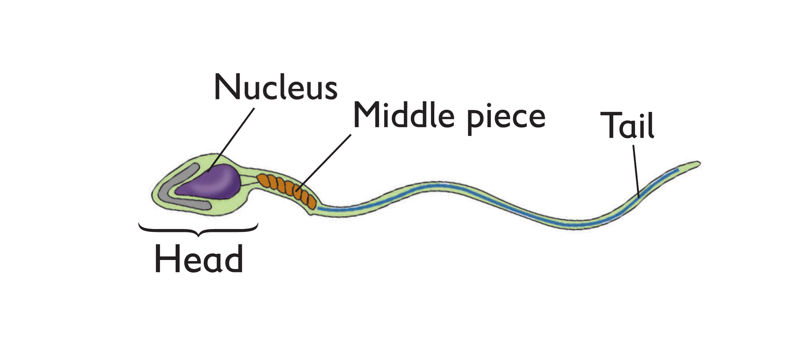
A sperm has three main parts:
- The head for penetrating the ovum. It contains chemicals that dissolve the wall of the egg (ovum) and nucleus which fuses with egg nucleus during fertilisation.
- Middle piece – Contain energy-producing molecules which keep the sperm in motion.
- The tail that propels the sperm.
Sperms are carried in a liquid called semen. The liquid is produced in the male sex glands. Its functions include:
- Transportation of sperms.
- Keeping the sperms moist.
- Providing nourishment to the sperms.
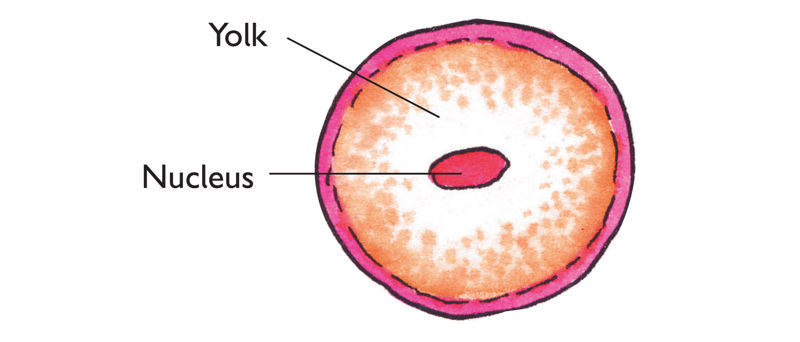
On the other hand when girls reach puberty, their reproductive systems become mature and start producing hormones as well. Also, their ovaries start producing eggs or ova (singular - ovum). The ovum has two main parts:
- The yolk which contains stored food for growth of the zygote.
- The nucleus which fuses with the sperm nucleus during fertilisation to form the zygote.
When a mature male and female engage in sexual intercourse immediately after ovulation, fertilisation occurs leading to pregnancy.
Remember: You should AVOID sexual intercourse! It may lead to unwanted pregnancy or HIV and AIDS infection.
