Specific objectives
By the end of this topic, you should be able to:
- Distinguish between continuous and discontinuous variations.
- Describe the structure and properties of chromosomes.
- State the first law of inheritance, and describe Mendel's work.
- Construct and use a punnet square/checker board.
- Distinguish between the following pairs: F1 and F2 generations, genotype and phenotype, haploidy and diploidy, homozygosity and heterozygosity, dominance and recessiveness, linkage and sex linkage, mutations and mutagens.
- Predict and explain the inheritance of the ABO blood groups and the rhesus (Rh) factor.
- State examples of genetically inherited disorders.
- Explain the causes of chromosomal mutations.
- Explain the practical application of genetics.
Brain teaser
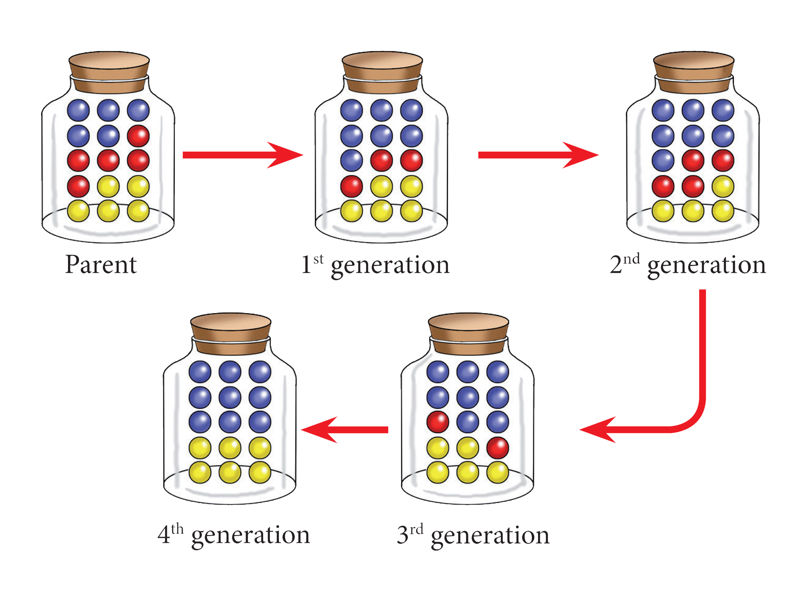
Study the pictures in Figure 1.1. Count the number of blue, red, and yellow marbles in each bottle. How many are there per generation?
Assuming that each colour represents a characteristic of an individual, can you note any trend in the characteristics as you move from one generation to another? Where do you think the red characteristic disappeared to in the 4th generation? Why did the number of blue characteristics in the 4th generation increase?
Assuming this is how inheritance occurs, what do you think genetics is all about?
In Form 3, you learnt about reproduction in plants and animals and the respective roles of mitosis and meiosis in asexual and sexual reproduction.
In this unit, you are going to learn how offsprings inherit characteristics from their parents. You will also examine the nature of the genetic material and how it determines the characteristics of an organism.
